What is Gastric Bypass Surgery?
Overview
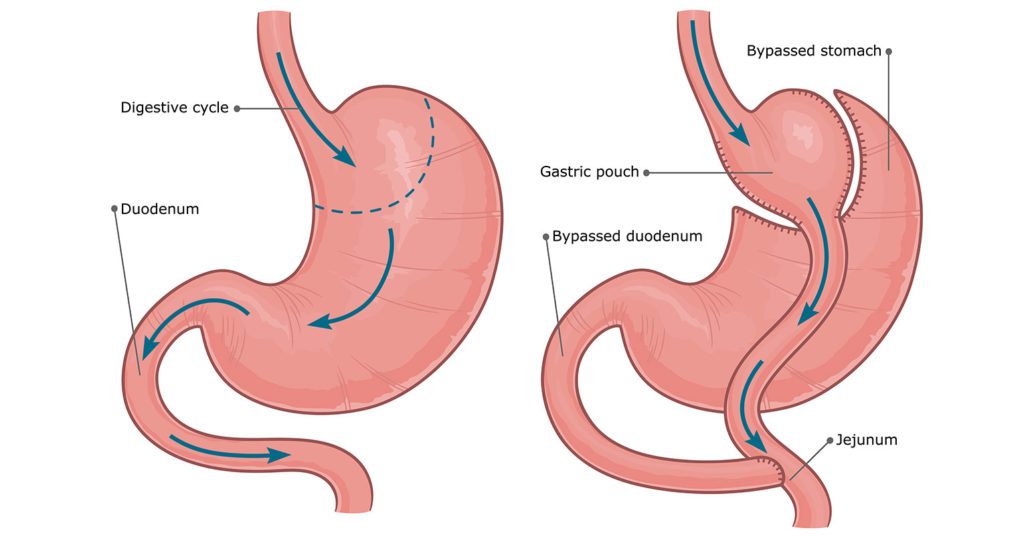
Gastric bypass surgery, also known as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, is a type of bariatric surgery designed to help individuals lose weight by changing how the stomach and small intestine handle food. The procedure involves creating a small stomach pouch and rerouting the small intestine to this pouch, limiting food intake and nutrient absorption.
How It Works
The surgery reduces the size of the stomach, making you feel full with less food. It also alters hormone levels, which may help reduce appetite. By limiting calorie intake and absorption, gastric bypass can lead to significant weight loss and improvement in obesity-related conditions.
Comparison with Other Bariatric Surgeries
-
Gastric Sleeve Surgery: Involves removing a portion of the stomach, creating a sleeve-like structure. It is less complex but also effective in weight loss.
-
Adjustable Gastric Banding: A band is placed around the upper part of the stomach to create a small pouch. It is less invasive but may lead to less weight loss compared to gastric bypass.
Comparison of Bariatric Surgeries
|
Surgery Type
|
Procedure Description
|
Potential Weight Loss
|
|
Gastric Bypass
|
Small stomach pouch and intestine rerouting
|
60-80% excess weight loss
|
|
Gastric Sleeve
|
Removal of a portion of the stomach
|
50-70% excess weight loss
|
|
Adjustable Gastric Banding
|
Banding the upper stomach to create a small pouch
|
40-50% excess weight loss
|
Data Source: American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery
Who is Eligible for Gastric Bypass Surgery?
Eligibility Criteria
-
Body Mass Index (BMI): Candidates typically have a BMI of 40 or more, or a BMI of 35-39.9 with obesity-related health conditions such as diabetes or hypertension.
-
Previous Weight Loss Attempts: Should have attempted other weight loss methods without success.
-
Health Assessment: Must undergo a comprehensive health assessment to ensure they are fit for surgery.
Psychological Evaluation
Candidates often undergo a psychological evaluation to ensure they have realistic expectations and understand the lifestyle changes required post-surgery.
Free Consultations and Evaluations
Many clinics in the United States offer free consultations to evaluate candidates for bariatric surgery. This helps prospective patients understand the procedure, benefits, risks, and post-operative commitments.
The Procedure: What to Expect
Pre-Operative Preparation
-
Medical Tests: Includes blood tests, imaging, and nutritional counseling.
-
Dietary Changes: Patients may need to follow a special diet leading up to the surgery.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Encouraged to quit smoking and limit alcohol intake.
Surgical Procedure
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia and typically takes 2-4 hours. Surgeons create a small stomach pouch and reroute the small intestine to this pouch, bypassing a portion of the digestive tract.
Post-Operative Care and Recovery
-
Hospital Stay: Patients usually stay in the hospital for 1-2 days post-surgery.
-
Dietary Progression: Begins with liquids, gradually progressing to pureed and soft foods before resuming regular meals.
-
Follow-Up Appointments: Regular check-ups to monitor progress and address any complications.
Stages of Recovery After Gastric Bypass Surgery
|
Stage
|
Duration
|
Key Focus
|
|
Immediate Post-Operative
|
1-2 days
|
Hospital recovery and initial monitoring
|
|
Liquid Diet
|
1-2 weeks
|
Hydration and initial healing
|
|
Pureed Foods
|
3-4 weeks
|
Gradual reintroduction of nutrients
|
|
Soft Foods
|
4-8 weeks
|
Transition to more solid foods
|
|
Regular Diet
|
8+ weeks
|
Balanced nutrition with portion control
|
Data Source: Mayo Clinic
Benefits and Risks
Benefits
-
Significant Weight Loss: Can lose up to 60-80% of excess weight within the first 12-18 months.
-
Improvement in Obesity-Related Conditions: Helps with conditions like type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and hypertension.
-
Enhanced Quality of Life: Many patients report improved mobility, self-esteem, and overall well-being.
Risks and Complications
-
Surgical Risks: Includes infection, blood clots, and adverse reactions to anesthesia.
-
Nutritional Deficiencies: Due to reduced absorption, patients need to take lifelong vitamins and supplements.
-
Dumping Syndrome: Rapid gastric emptying causing nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea when eating certain foods.
Alternatives to Gastric Bypass Surgery
Gastric Sleeve Surgery
Less complex than gastric bypass, this procedure involves removing a portion of the stomach to create a sleeve. It offers significant weight loss with a reduced risk of nutritional deficiencies.
Adjustable Gastric Banding
This minimally invasive procedure places a band around the stomach to limit food intake. It requires regular adjustments and offers a slower weight loss process compared to gastric bypass.
Non-Surgical Weight Loss Programs
-
Diet and Exercise: Comprehensive lifestyle changes focusing on nutrition and physical activity.
-
Medical Weight Loss: Supervised programs involving medications, counseling, and nutritional support.
Alternatives to Gastric Bypass Surgery
|
Alternative
|
Description
|
Pros and Cons
|
|
Gastric Sleeve Surgery
|
Removal of stomach portion
|
Pros: Less complex; Cons: Irreversible
|
|
Adjustable Gastric Banding
|
Band around stomach
|
Pros: Less invasive; Cons: Slower weight loss
|
|
Non-Surgical Weight Loss
|
Diet, exercise, medical programs
|
Pros: Non-invasive; Cons: Requires discipline
|
Data Source: Obesity Action Coalition
Choosing the Right Bariatric Surgery
Factors to Consider
-
Health Conditions: Assess existing health issues that may influence the choice of surgery.
-
Weight Loss Goals: Consider how much weight loss is desired and the time frame.
-
Lifestyle: Evaluate willingness and ability to adhere to post-operative lifestyle changes.
Consulting with Bariatric Experts
Free consultations with bariatric experts in the United States can provide valuable insights into the most suitable procedure based on individual health profiles and preferences.
FAQs
What is gastric bypass surgery?
Gastric bypass surgery is a bariatric procedure that reduces stomach size and reroutes the small intestine to promote weight loss and improve obesity-related health conditions.
Who is eligible for gastric bypass surgery?
Candidates typically have a BMI of 40 or more, or a BMI of 35-39.9 with obesity-related health issues, and must have attempted other weight loss methods without success.
What are the risks of gastric bypass surgery?
Risks include surgical complications such as infection and blood clots, as well as post-operative issues like nutritional deficiencies and dumping syndrome.
How does gastric bypass compare to other weight loss surgeries?
Gastric bypass often results in more significant weight loss compared to banding but involves more complex surgery. Gastric sleeve offers a middle ground with less complexity.
What factors should be considered when choosing a bariatric surgery?
Considerations include existing health conditions, weight loss goals, and the ability to commit to lifestyle changes post-surgery.
Gastric bypass surgery offers a transformative opportunity for weight loss and improved health for individuals struggling with obesity. By understanding the procedure, eligibility, benefits, risks, and alternatives, patients can make informed decisions about their health journey. Consulting with qualified bariatric experts and considering personal health profiles will aid in choosing the most suitable approach for achieving long-term success.